INFORMATION
A-F
4:0 or 4:1 or 4:4 etc
Refers to the number of colours used per side.
Can be referred to as four back zero / four back one / four back four.
4 Colour Process - See CMYK
A-Sizes
The most common paper sizes used for stationery, leaflets and other publications - See above
Art Board/Paper
A term used for coated papers
Artwork
The images/text that are to be printed (usually supplied digitally as a PDF).
As a general rule, artwork refers to images/text that are print ready and should be supplied as a high resolution PDF at 300 dpi (actual Size), with crop marks and 3mm bleed or as a Vector eps/Illustrator(ai) file.
Bleed
Where the image to be printed extends (usually by 3mm) over the crop marks. This makes trimming easier and means the finished documents will run to the edges
Blind Emboss
A type of embossing where no ink is used. Instead, the design or text is only visible as a raised area on the paper/card. Also see debossing which has the opposite effect
Bond Paper
Strong, uncoated paper often used for stationery
C-Sizes
Paper sizes used for envelopes. These correspond to A-sizes (e.g. C4 envelope will hold A4 sheets)
C3 - 324 x 458 mm C4 - 229 x 324 mm
C5 - 162 x 229 mm C6 - 114 x 162 mm
DL - 110 x 220 mm (holds A4 folded twice)
CMYK
Abbreviation of Cyan, Magenta, Yellow and Black.
These make up the standard 4 colour process used for printing in full colour
Coated Paper
Paper which has a coating on one or both sides. This can have a gloss or silk (matt) finish. Coated papers are used for the majority of printed products, but not for stationery where an uncoated (or bond) paper is used
Crop Marks
Lines marking where the paper is to be trimmed after printing. These should be part of the artwork
Cutting Forme (or Die)
The custom made cutter used when die-cutting
Debossing
Where an image is pressed or stamped into the paper creating a depression as opposed to an embossed, raised impression
Die-cut
Where an irregular shape is cut from the paper instead of trimming square edges. This can be any shape but requires a die or cutting forme to be made up specially
Digital Printing
Low cost method of printing best suited for short run jobs. It works directly from electronic data without the need for printing plates. This makes the process very quick but the print quality, although a good alternative is not on par with lithography. Also, you can not use specific spot colours or metallic inks. Generally good for 500 or less.
DPI
Dots per inch, or the image resolution. For print, all images in a document should always be a minimum of 300dpi - see resolution
Dummy/Mockup
A Mock up of the finished product. This can be printed or unprinted, depending on the purpose. See proofs
Embossing
Where designs are pressed in to the paper to leave a raised effect
EPS (Encapsulated Postscript)
the most widely used file format for graphics which are to be included in page-layout and text files.
Foil Blocking
Where a design is stamped into the cover, usually in a metallic foil
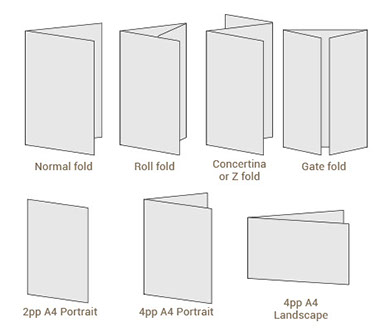
Folding
There are a large number of different folding options. Some common folds are:
Full Colour
Printing in CMYK, as opposed to using spot colours. Although you can print full colour with additional spot colours
G-V
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format)
Graphic image file format used on the web, may be a static image or a simple animation. Also good for Powerpoint files as they are small and can have transparent backgrounds
Gloss coated paper
These papers have a smooth surface and a high shine, perfect for producing printed promotional items e.g brochures, flyers and leaflets.
GSM
Grams per square metre. This is the standard measurement of weight for paper.
HEX
Hex codes are ways of representing colors in a format that can be understood by computers. Mainly used for websites and eshots etc. eg. #3a297c
Imposition
The pages of the artwork are arranged such that after printing, cutting and folding, the pages will be in the correct order. Sometimes seen when an imposition proof is supplied electronically, the pages will not be in chronological order.
JPEG (Joint Photographic Expert Group)
Generally a photographic or tonal image in digital format, viewable on any platform
Laminating
Where a thin plastic film is fixed to one or both sides of the paper. This can create a silky matt or a high gloss finish, depending on the intended purpose and personal preference. It also acts as a protective barrier if the print needs to be more durable or is likely to encounter a demanding environment
Landscape
Where a document is oriented so the long edges are at the top and bottom. As opposed to portrait
Lithography / Lithographic (or litho)
The most popular print process, a metal plate is treated so that the image area attracts the oil-based inks, while the wet non-image areas resist them
Origination
The files to be printed which make up the artwork. Usually a print ready PDF
Page
One side of a sheet of paper. For example, an A4 sheet has 2 pages. An A4 sheet folded in half to A5 has 4 pages.
PDF- Portable Document Format.
Universal file format which combines images and text. These can be saved as Low Res or High res Print files - See file name above.
Perfect Binding
Where the text pages are glued in to the cover. See also burst binding.
PMS
Pantone Matching System. Followed by 3 or 4 digits to make up a code e.g. PMS 072.
See spot colours
PNG (PNG-24) Portable Network Graphics
The ideal web graphic file types. They are completely lossless and they support alpha transparency. PNG-8 is essentially a GIF. Also good for Powerpoint files as they are small and can have transparent backgrounds
Portrait
Where a document is oriented so the long edges are on either side. As opposed to landscape
PP
Printed pages. Refers to the number of pages in a document e.g. 12pp (12 pages)
Proof
Proofs are an example of what is to be printed so both parties are in agreement. Any errors or amendments should be picked up at this stage. This can take the form of a digital proof, usually supplied as a PDF, or a printed proof. See digital proofs and wet proofs for more details
PSD
Photoshop Document extension. A design program used to manipulate raster (bitmap) images.
Raster image - see also Vector Images
There are two kinds of digital images. A raster image is made up of individual pixels. When you try to enlarge a raster image it looks pixelated because you are taking each block of information (pixel) and just making it bigger. Raster images are often created in programs like Photoshop and have the extension JPG. TIFF or .GIF. Tiff. PNG
Resolution
Resolution is a measure of dots per inch (DPI) for printed works and pixels per inch (PPI) for digital work. If the resolution of an image is too low, your final product will come out looking grainy or pixelated.
Images for litho print should generally be 300 DPI at the size you wish to use the image. If the images are to be printed digitally or for Large format print you can sometimes you can get away with a lower resolution.
72DPI for web work or viewing on screen.
If in doubt talk to your designer.
Screen Printing
The oldest method of printing. Ink is applied to a porous silk screen and passes through a stencil or template to leave an impression. Normally used when printing on fabric and banners and when printing on board that is too thick to pass through a standard litho print press
Self-Cover
Where the cover and text pages are on the same paper stock.
Silk Coated Paper
Silk papers have a low surface shine, a smooth finish, but not glossy.
Spot/special Colours
Refers to solid colours which are found in commercially obtainable colour ranges such as Pantone®, these are mostly used in addition to CMYK where CMYK is not available e.g. Printing gold or silver. When using Pantone colours, it is worth bearing in mind for future jobs that should you want to print in CMYK, the chosen Pantone® may not have a suitable CMYK equivalent, which may in turn lead to the expense of using additional plates.
Spot Gloss UV Varnish
A high gloss finish applied to specific areas of print. This differs from gloss laminating which has to cover the whole sheet
TIFF (Tag Image File Format)
File format used to store large non-compressed image files, generally used for high resolution print.
Uncoated Paper
Paper which has not been coated, not gloss or silk
Vector images - see also Raster images
A vector image is made up of points connected along a curve (or vector). The image can be expanded to an infinite size. Vector images are created in programs like Illustrator and have the file extension .EPS. AI.
Note EPS’s can also be resolution based Raster images if created/saved in photoshop.